TBI: General Information, Articles
Traumatic brain injuries are one of the most common causes leading to death in people under the age of 45. Accidental TBIs occur every 15 seconds. They lead to numerous complications.
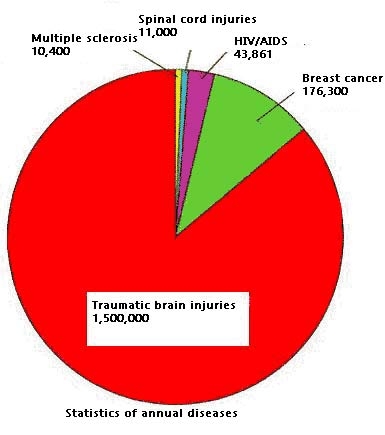
This section includes various information related to TBI:
Research results:
- TBI contributes to the development of Parkinson’s disease
- Statins will help treat traumatic brain injury
- Smell and taste after TBI
- Hearing after TBI
- Importance of otoneurological examination
The main causes of TBI include motor vehicle accidents, falls and sports injuries. Despite the fact that the brain is enclosed in a secure skull membrane, it is very vulnerable.
Concussion is an instant failure of the brain. It is the mildest form of the traumatic brain injury with a brief loss of consciousness. When patients regain consciousness they complain of headache, dizziness, nausea and vomitin. Tinnitus, sweating, sleep disorder are common as well. The vital bodily functions do not suffer any significant deviations. Patient’s general condition usually improves during the first, rarely the second day. If any symptoms are found, the patient should be examined to rule out the possibility of the concussion. This TBI is treatable.
Unfortunately, there are no clear signs that can indicate an irreversible damage to the brain due to a certain trauma. To diagnose this disease in time, doctors take into account any complaints and symptoms that patient have.
Here are some of them:
Each patient has a different rehabilitation period. It depends on the type of the injury and the degree of brain damage. All necessary procedures are prescribed to each patient individually. The goal of rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury is to restore as many lost brain functions as possible. The program includes therapy that aims to restore vital functions, namely speech and movement. In addition, the specialists help patients to overcome complications caused by incurable traumas, as well as develop certain methods, which can compensate lost abilities developed due to the improper functioning of the CNS.
Traumatic brain injury can affect any area and function of the brain. A failure in the work of the brain leads to excessive drowsiness, attention defecit, difficulty concentrating, memory disorder, depression, irritability, emotional outbursts, sleep disorders, a low libido, difficulties in switching between two tasks and slow thinking.
Unfortunately, head injuries in children are quite common. An annual number of hospitalizations accounts for approximately one hundred thousand traumatic brain injury cases affecting children. The causes of such injuries are road accidents, bike falls, sports injuries, falls from a height and child abuse. There are some features peculiar only to children's injuries. Both symptoms and effects of traumatic brain injuries in children are very different from those of adults. For example, it is much more difficult to determine the degree of brain damage and any possible dysfunctions in a child. After analyzing the results of studies at school and higher educational institutions, the coefficient of mental development and professional activity (for adults), doctors can determine the severity of the injury. At one time it was believed that children are more resistant to brain injuries than adults, because their growing brain could restore itself faster over time. However, more and more studies point to the opposite. In fact, compared with adults, children are more susceptible to irreversible brain damage, even if the force of the blow is the same.
During the research, it was found that TBI is one of the key factors leading to the destruction of neurons directly related to the development of Parkinson's disease.
The use of statins in case of the head injury prevents complications and sometimes even death among middle-aged and elderly people.
The methods of examining smell disorders in patients with traumatic brain injuries are divided into objective and subjective, as well as into qualitative and quantitative. Severe patients with acute TBI are examined by means of the Borchtein’s method. The procedure is quite simple and the patient should be conscious when undergoing this examination. The test involves the use of the following set of odorous substances:
In case of traumatic brain injury, hearing loss is most commonly caused by the cracks in the pyramid of the temporal bone. The less common causes of hearing loss include traumatic damages to the central auditory pathways in the nuclear region (in this case, hearing loss develops on the affected side) or traumatic damages to the middle brain (hearing loss occurs from two sides and more greatly affects the spoken language).



